We all know that the skin heals and grows on its own when we experience a wound because our body has the ability to replace damaged skin cells. But, what when one experiences deep second and full-thickness burns on a larger part of their skin!? We have heard of accidents caused by fires, and cases of acid attacks. The life of these people is nothing less than hell after they experience such a situation. No doubt there are plastic surgeries for such patients, but not everyone can afford them. Medical science has now brought about a new innovation for such victims – grafting – thanks to the clinical research industry. This gives one the ability to grow one’s own skin in a lab, making it a breakthrough for burn patients and experts who treat them.
The skin is the largest organ of the body, accounting for up to 15% of a person’s total body weight. It guards the underlying bones, muscles, and internal organs, while providing insulation, temperature regulation, and sensory capabilities. The skin is thus an incredible part of the body structure. Surgeons can help this incredible organ grow by using the patient’s own skin cells through skin grafting.
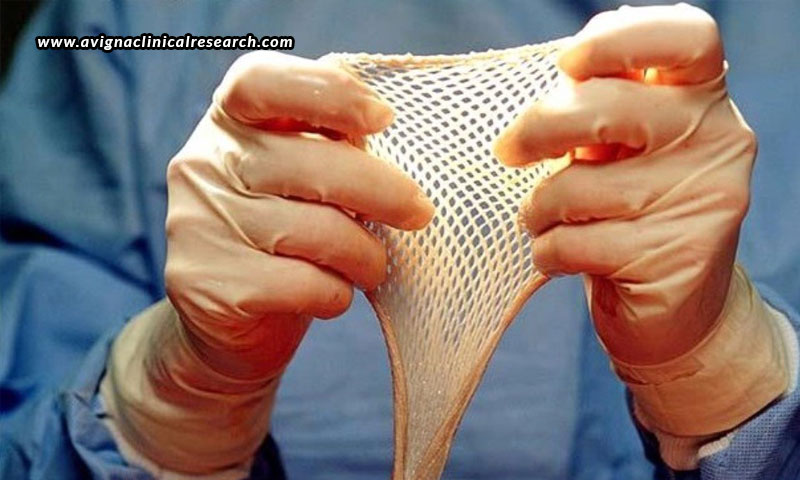
Skin grafting is done in a surgical procedure that consists of removal of the injured tissue, selection of a donor site, removal of the graft, and placement and securing of the graft. First, a small graft of healthy skin of the size of a postage stamp is taken from the patient, which then goes through a sophisticated culture process to promote cell growth and creation of a sufficient number of sheets of skin that can be grafted on the patient to restore the vital skin. In this way, skin is removed from one area of the body and transplanted to another.
The process involves a special skin-cutting instrument known as a Dermatome that removes skin from one area like the inner thigh or buttocks. The graft is then placed where required, which is held in place by a dressing and a few stitches. The donor site is also covered with dressing to prevent any kind of infection. Surgical staples are also used to secure the edges of the graft. Once the edges have healed and the graft is stable, the staples are removed. It takes around three to six weeks for the patient to recover from such grafting. To help the graft heal more effectively, the area of the graft is not moved for five days after the surgery. During this period, the blood vessels begin to grow from the tissue below into the donor skin, bonding the two layers together. After this, the doctor prescribes exercise therapy programs and tub baths along with medications.
When the burn areas are severe, deep, and large, the wounds and trauma are considered as one of the most serious attacks to the skin as it causes the skin cells to die. Thus, this grafting technique has proven to be a boon for such patients. And, this has all been possible because of the clinical research field. You can also help such patients and your country mates by undertaking official clinical research online training in Bangalore from an institute like Avigna Clinical Research Institute, where you can learn from the comfort of your home and gain a legitimate degree that is valid throughout the country.